Even if sales increase, fixed costs do not change, hence causing a larger change in operating income. If sales revenues decrease, operating income will decrease at a much larger rate. It is important to understand that controlling fixed costs can lead to a higher DOL because they are independent of sales volume.
DOL and Operating income
This is the financial use of the ratio, but it can be extended to managerial decision-making. Essentially, operating leverage boils down to an analysis of fixed costs and variable costs. Operating leverage is highest in companies that have a high proportion of fixed operating costs in relation to variable operating costs. Conversely, operating leverage is lowest in companies that have a low proportion of fixed operating costs in relation to variable operating costs. A corporation will have a maximum operating leverage ratio and make more money from each additional sale if fixed costs are higher relative to variable costs. On the other side, a higher proportion of variable costs will lead to a low operating leverage ratio and a lower profit from each additional sale for the company.
Do you own a business?

The DOL ratio assists analysts in determining the impact of any change in sales on company earnings or profit. Operating leverage measures a company’s fixed costs as a percentage of its total costs. It is used to evaluate a business’ breakeven point—which is where sales are high enough to pay for all costs, and the profit is zero. A company with high operating leverage has a large proportion of fixed costs—which means that a big increase in sales can lead to outsized changes in profits.
Would you prefer to work with a financial professional remotely or in-person?
In other words, greater fixed expenses result in a higher leverage ratio, which, when sales rise, results in higher profits. A low DOL, on the other hand, suggests that a company’s variable costs are higher than its fixed costs. This means that changes in sales have a less staff accountant job description dramatic impact on operating income. Companies with low operating leverage experience smaller fluctuations in EBIT with changes in sales. This structure provides stability, as lower fixed costs mean the company doesn’t require high sales volumes to cover its expenses.
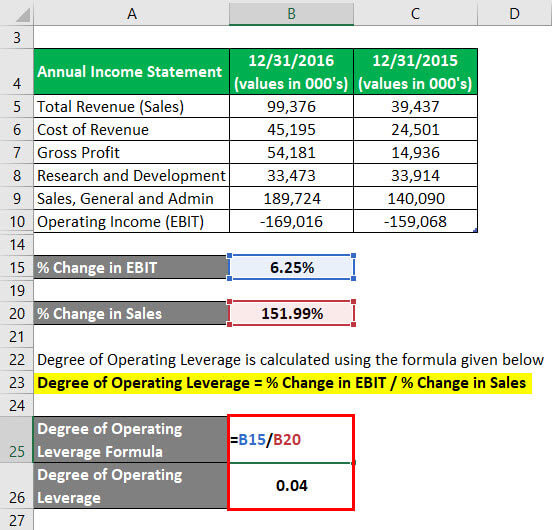
Operating Leverage Analysis Example
It is a key ratio for a company to determine a suitable level of operating leverage to secure the maximum benefit out of a company’s operating income. The formula is used to determine the impact of a change in a company’s sales on the operating income of that company. DCL is a more comprehensive measure of a company’s risk because it takes into account both sales and financial leverage. As such, the DOL ratio can be a useful tool in forecasting a company’s financial performance. Degree of operating leverage closely relates to the concept of financial leverage, which is a key driver of shareholder value.
How to Calculate Earnings Per Share? (Definition, Using, Formula)
Increasing utilization infers increased production and sales; thus, variable costs should rise. If fixed costs remain the same, a firm will have high operating leverage while operating at a higher capacity. Operating leverage occurs when a company has fixed costs that must be met regardless of sales volume. When the firm has fixed costs, the percentage change in profits due to changes in sales volume is greater than the percentage change in sales.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master’s in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology.
- Companies with high degrees of operating leverage experience more significant changes in profit when revenues change.
- This variation of one time or six-time (the above example) is known as degree of operating leverage (DOL).
- Because Walmart sells a huge volume of items and pays upfront for each unit it sells, its cost of goods sold increases as sales increase.
- The Operating Leverage measures the proportion of a company’s cost structure that consists of fixed costs rather than variable costs.
- For example, the DOL in Year 2 comes out 2.3x after dividing 22.5% (the change in operating income from Year 1 to Year 2) by 10.0% (the change in revenue from Year 1 to Year 2).
Companies with high fixed costs tend to have high operating leverage, such as those with a great deal of research & development and marketing. With each dollar in sales earned beyond the break-even point, the company makes a profit. Conversely, retail stores tend to have low fixed costs and large variable costs, especially for merchandise. Because retailers sell a large volume of items and pay upfront for each unit sold, COGS increases as sales increase. One concept positively linked to operating leverage is capacity utilization, which is how much the company uses its resources to generate revenues.
Finally, it is essential to have a broad understanding of the business and its financial performance. That’s why we highly recommend you check out our otherfinancial calculators. Get instant access to video lessons taught by experienced investment bankers.




